Process-related impurities in the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine (preprint, 2021)
(Astrazeneca)
Any extracts used in the following article are for non commercial research and educational purposes only and may be subject to copyright from their respective owners.
Abstract
Sinus venous thrombosis has been linked to immunization with the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine. The initial trigger for this serious adverse event has not been determined. We analyzed the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine by biochemical and proteomic methods. We found that the vaccine, in addition to the adenovirus vector, contains substantial amounts of both human and non-structural viral proteins. Among the human proteins, heat-shock proteins and cytoskeletal proteins were particularly abundant. The often-observed strong clinical reaction one or two days after vaccination is likely associated with the detected protein impurities. A linkage to later immune-related adverse events is also conceivable. The here reported identification of specific classes of protein impurities should guide and accelerate efforts to increase the purity of the vaccine and increase its safety and efficacy.
“Previously, it has been shown, that simian adenovirus vectors including ChAdOx1 can be purified at high yield and purity using such technology for purification 8. Although in our experiment the same number of particles was loaded, the staining patterns looked very different (Fig. 1). While staining of HAdV-C5-EGFP proteins resulted in the expected pattern, representing distinct major capsid proteins of HAdV-C5 including Hexon, Penton Base, IIIa and Fiber, silver staining of separated proteins from three different lots of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 showed a large number of bands with different intensities, many more bands than could be explained by proteins from viral particles.”
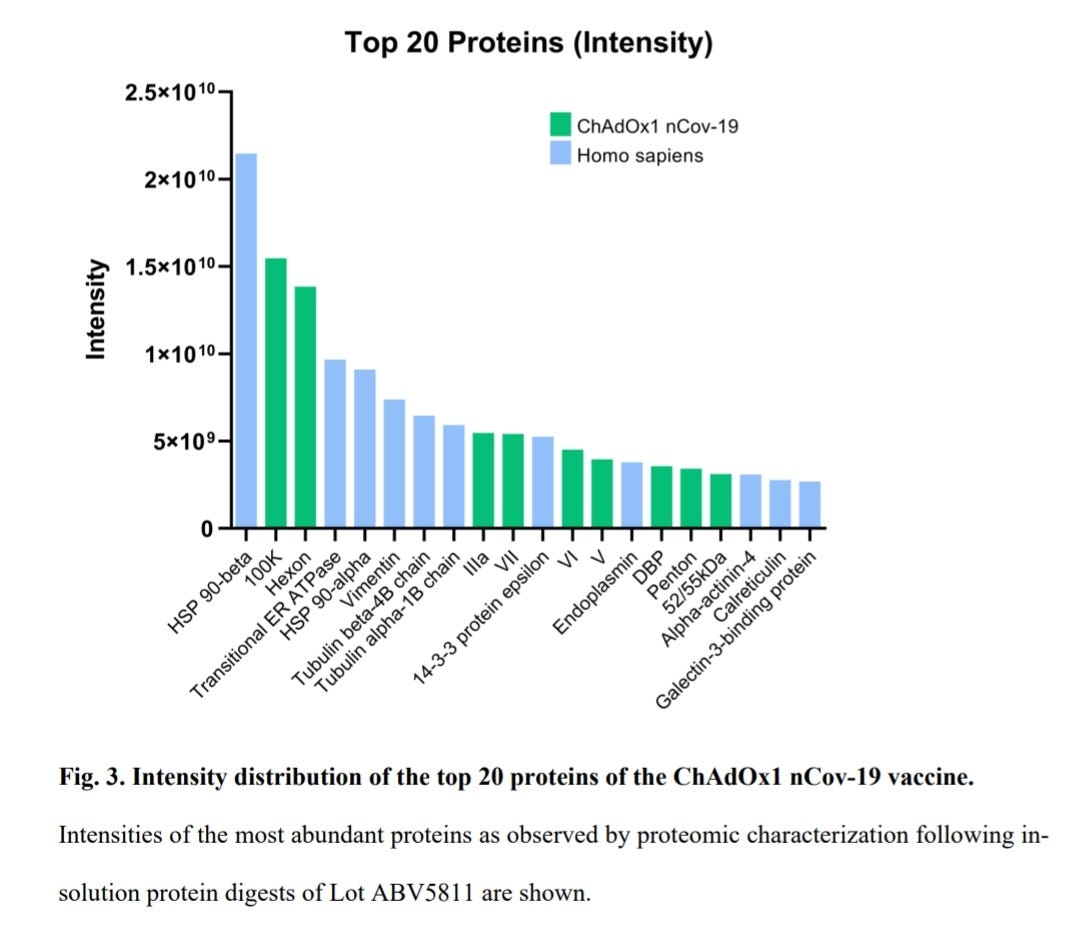
“We analyzed all three vaccine charges in detail at the proteomic level. The protein content of a single vaccine dose of 0.5 ml of lot ABV5811, containing 5 x 1010 viral particles according to the specification, was determined to be 32 µg. This was considerably more than the 12,5 µg protein that would be expected in one dose based on the known 150 MDa molecular weight (MW) of adenovirus 9.”
“Peptides from more than 1000 different human proteins were detected being derived from the human vector production cell lines”.
“Intriguingly, from the human proteins found in the vaccine and beside several cytoskeletal proteins including Vimentin, Tubulin, Actin and Actinin, the group of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and chaperones stood out in abundancy. Among the top abundant proteins (including viral proteins) HSP 90-beta and HSP-90-alpha as cytosolic HSPs (with 9.5 % and 4.3 % of the total protein) and 3 chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum (transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase, Endoplasmin and Calreticulin) were present (Fig. 3 and Suppl. Table S2). Of note, also the abundant adenoviral non-structural 100K protein has chaperone function. Like many viruses, adenovirus has been reported to induce HSPs during amplification in production cells 10, likely to accommodate for a need in help by HSPs in the folding and production of large amounts of structural and non-structural viral proteins and in virion assembly. Thus, virus infection-mediated induction of HSPs could contribute to the abundancy of HSPs in the vaccine product in case of insufficient purification.”
“The injection of the vast majority of the more than 1000 different proteins contained in the vaccine is not expected to result in adverse effects. However, some of the detected proteins might be more than inert bystanders. Extracellular HSPs modulate innate and adaptive immune-responses, can exacerbate pre-existing inflammatory condition, have been associated with autoimmunity and can even become target auf auto-immune responses themselves 12-14”
“Several of the HSPs also have ATPase activity and might directly be involved in the activation of platelets by the generation of ADP after intramuscular injection of the vaccine into the ATP-rich skeletal muscle. Among the viral proteins detected, the adenoviral penton base is another candidate for inducing early toxicity via an RGD motive, present in a solvent-exposed loop of penton base, by interacting with integrins on cell membranes including of platelets. Thus, we consider it likely that the here documented protein impurities are involved in the strong clinical reactions with flu-like symptoms, very often observed one or two days after vaccination.”
“With the many different contaminant proteins detected in the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine and therefore an immanent uncertainty, whether or not (some of) the impurities might have long-term immune-related side effects, it is necessary to improve the purification process for the vaccine to potentially increase its safety and reduce concerns. This might have the additional benefit of also enhancing the antiviral efficacy of the vaccine.
The establishment of robust assays for detection of HCPs can be complicated and very time-consuming 16, in particular if processes for new and complex biopharmaceuticals have to been developed, time that maybe is not always available in times of a pandemic. However, the identification of specific process-related impurities in ChAdOx1 nCov-19, as reported here, should guide and accelerate the required next steps.”
Full paper:
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-477964/v1
PDF download:
https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-477964/v1_stamped.pdf
Pathology:
Heat Shock Proteins, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease (2002)
Hsp Expression and Hsp Reactivity in Vascular Disease
“Although the precise influence of hsps on atherogenesis and atherosclerosis is unclear, an association between expression of and reactivity to hsps and induction of the inflammatory response that characterizes the development of atherosclerosis has arisen from a number of studies. The intensity of hsp expression positively correlates with the severity of atherosclerosis; there is a localized enrichment of γ/δ T cells, which have a predisposition to respond to hsps, in the lesion36; and immunization with recombinant mycobacterial hsp65 can induce atherosclerotic lesions in normocholesterolemic rabbits,37 normal C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet,38 and LDL-receptor–deficient mice.39
Raised levels of anti-hsp antibodies have also been associated with the presence and progression of vascular disease. Elevated levels of circulating antibody to the mycobacterial 65-kDa hsp have been reported in carotid atherosclerosis,40 coronary heart disease,41 and borderline hypertension,42,43 and levels of antibodies to human hsp60 are increased in peripheral vascular disease.44 Levels of anti-hsp65 antibodies might have some diagnostic value, because titers appear to predict the 5-year mortality of patients with carotid atherosclerosis.45”
Full paper:
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/hc0802.103729
Role of Hsp90 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Its Clinical Relevance
04 Oct 2012
Abstract
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a family of ubiquitous and phylogenically highly conserved proteins which play an essential role as molecular chaperones in protein folding and transport. Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) is not mandatory for the biogenesis of most proteins, rather it participate in structural maturation and conformational regulation of a number of signaling molecules and transcription factors. Hsp90 has been shown to play an important role in antigen presentation, activation of lymphocytes, macrophages, maturation of dendritic cells, and in the enhanceosome mediated induction of inflammation. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease with complex immunological and clinical manifestations. Dysregulated expression of Type I interferon α, activation of B cells and production of autoantibodies are hallmarks of SLE. The enhanced levels of Hsp90 were detected in the serum of SLE patients. The elevated level of Hsp90 in SLE has also been correlated with increased levels of IL-6 and presence of autoantibodies to Hsp90. This suggests that Hsp90 may contribute to the inflammation and disease progression and that targeting of Hsp 90 expression may be a potential treatment of SLE. The pharmacologic inhibition of Hsp90 was successfully applied in mouse models of autoimmune encephalomyelitis and SLE—like autoimmune diseases. Thus targeting Hsp90 may be an effective treatment for SLE, especially if combined with other targeted therapeutic approaches.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/728605
In responding to a question about the source of contamination I can confirm the HSPs came from foetal derived kidney cells from the HEK 293 cell line. And sad to say this uncovered a further, serious potential pathology: facilitation or maintenance of neoplastic transformation, ie cancer development.
“Foetal cells are used to make the Oxford coronavirus vaccine. But they came from a foetus in 1973 “(2020)
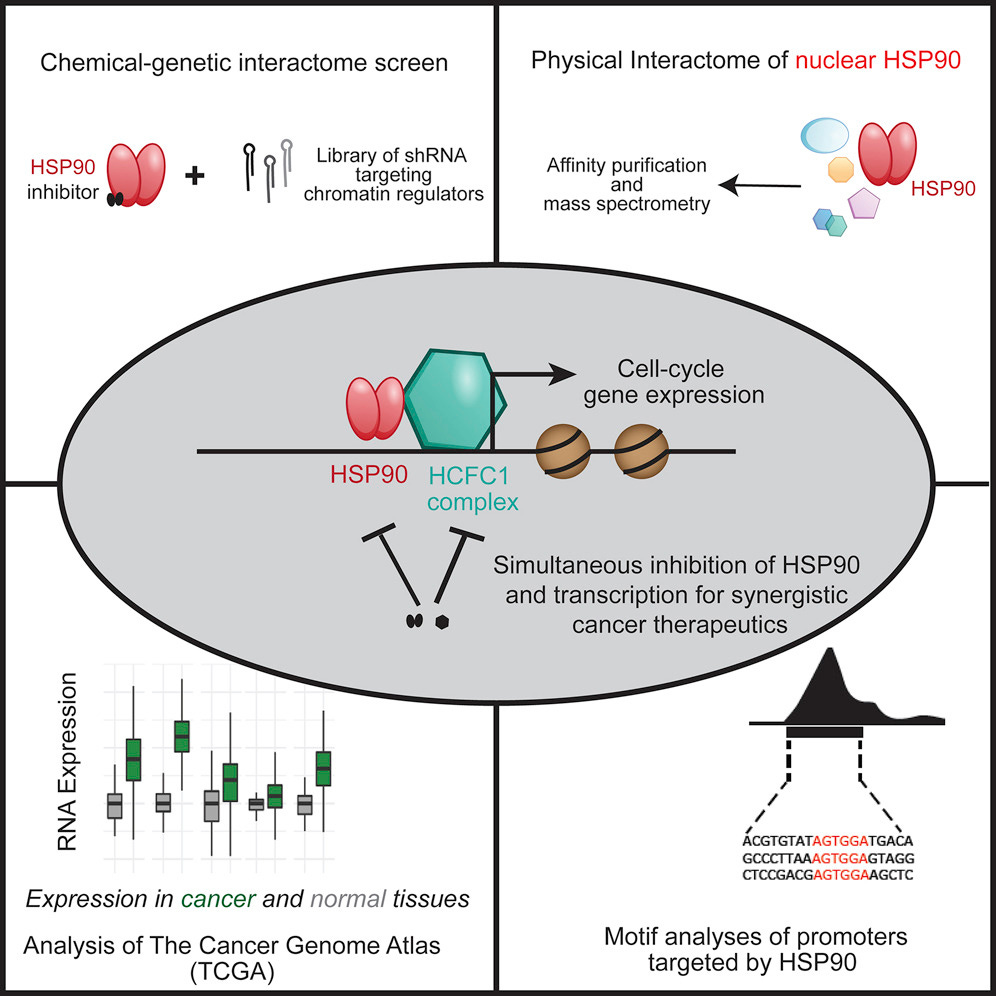
Heat-Shock Protein 90 Controls the Expression of Cell-Cycle Genes by Stabilizing Metazoan-Specific Host-Cell Factor HCFC1 (2019)
Summary
Molecular chaperones such as heat-shock proteins (HSPs) help in protein folding. Their function in the cytosol has been well studied. Notably, chaperones are also present in the nucleus, a compartment where proteins enter after completing de novo folding in the cytosol, and this raises an important question about chaperone function in the nucleus. We performed a systematic analysis of the nuclear pool of heat-shock protein 90. Three orthogonal and independent analyses led us to the core functional interactome of HSP90. Computational and biochemical analyses identify host cell factor C1 (HCFC1) as a transcriptional regulator that depends on HSP90 for its stability. HSP90 was required to maintain the expression of HCFC1-targeted cell-cycle genes. The regulatory nexus between HSP90 and the HCFC1 module identified in this study sheds light on the relevance of chaperones in the transcription of cell-cycle genes. Our study also suggests a therapeutic avenue of combining chaperone and transcription inhibitors for cancer treatment.
“Cancer cells were found to be more sensitive than normal cells to small-molecule inhibitors of the ATPase activity of HSP90, prompting several clinical trials in cancer patients.”
“HSP90 facilitates and/or maintains neoplastic transformation, causing an increased dependence of cancers on the HSP90 chaperone system. The precise mechanism by which HSP90 supports tumor proliferation remains ill-defined, but likely involves chaperoning a number of oncogenic drivers.”
Full paper:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124719312884







A few months ago there was a German lab, that analyzed the Astra Zeneca injections and found that impurities made up up to 65 prrcent(!) Of the contents of the vials. They sent their results to Astra Zeneca but did not hear anything back.