Spike protein (inc vax) induced immunodeficiency & carcinogenesis megathread #24:Decoding COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Immunometabolism in Central Nervous System:
Human brain normal glial and glioma cells by Raman imaging (preprint, 2022)
Any extracts used in the following article are for non commercial research and educational purposes only and may be subject to copyright from their respective owners.
Background:
Inhibiting apoptosis is a key feature of tumorogenesis. May we expect to see more cases of glioblastoma, and aggressive relapses as a consequence?
These transfection agents must be stopped being administered immediately, pending further investigations.
Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration (2008)
Key Points
Cytochrome c is one of the mitochondrial proteins that is released into the cytosol when the cell is activated by an apoptotic stimulus.
In the cytosol, cytochrome c engages the apoptotic protease activating factor-1 (APAF1), and forms the apoptosome, which activates caspase-9.
The release of cytochrome c has been suggested to occur in two phases: mobilization from the mitochondrial intermembrane space and translocation through the outer mitochondrial membrane.
The mechanisms of cytochrome c release are controversial. Whether the permeabilization of the outer or the inner membrane is responsible for the downstream events is one of the debated topics. Most evidence supports a model in which the outer membrane is permeabilized without inner membrane events.
The release of cytochrome c and cytochrome-c-mediated apoptosis are controlled by multiple layers of regulation, with the most prominent players being members of the B-cell lymphoma protein-2 (BCL2) family.
Abstract
Cytochrome c is primarily known for its function in the mitochondria as a key participant in the life-supporting function of ATP synthesis. However, when a cell receives an apoptotic stimulus, cytochrome c is released into the cytosol and triggers programmed cell death through apoptosis. The release of cytochrome c and cytochrome-c-mediated apoptosis are controlled by multiple layers of regulation, the most prominent players being members of the B-cell lymphoma protein-2 (BCL2) family. As well as its role in canonical intrinsic apoptosis, cytochrome c amplifies signals that are generated by other apoptotic pathways and participates in certain non-apoptotic functions.
https://www.nature.com/articles/nrm2434
JAK-STAT signaling pathway
The JAK-STAT signaling pathway is a chain of interactions between proteins in a cell, and is involved in processes such as immunity, cell division, cell death and tumour formation. The pathway communicates information from chemical signals outside of a cell to the cell nucleus, resulting in the activation of genes through a process called transcription. There are three key parts of JAK-STAT signalling: Janus kinases (JAKs), signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins (STATs), and receptors (which bind the chemical signals).[1] Disrupted JAK-STAT signalling may lead to a variety of diseases, such as skin conditions, cancers, and disorders affecting the immune system.[1]
More:
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/JAK-STAT_signaling_pathway
The paper:
Pay particular attention to section 3.3 & figure 7, in the light of the recent evidence that LINE-1 reverse transcription by BNT162B2 is indeed occurring.
The authors weren't expecting it but also found evidence of this due to cytochrome c downregulation in the nucleus.🤦♂️
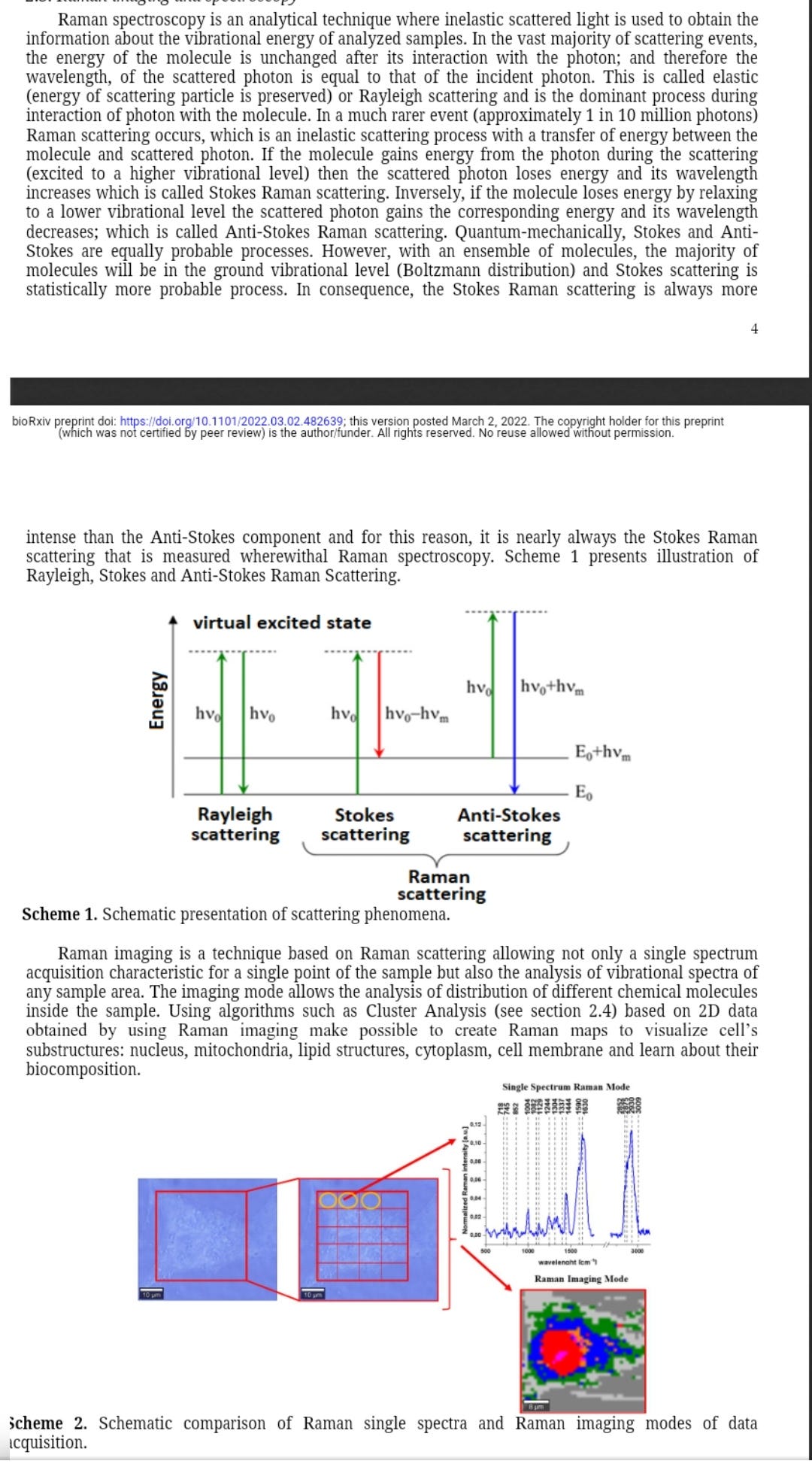
A new technique, Raman imaging uses light scatter as a non destructive way to analyse molecular distribution in cells and organelles.
Nothing to do with ramen noodles, but wouldn't say no.
Decoding COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Immunometabolism in Central Nervous System: human brain normal glial and glioma cells by Raman imaging
VlHalina Abramczyk, Beata Brozek-Pluska, Karolina Beton
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.02.482639This article is a preprint and has not been certified by peer review
Abstract
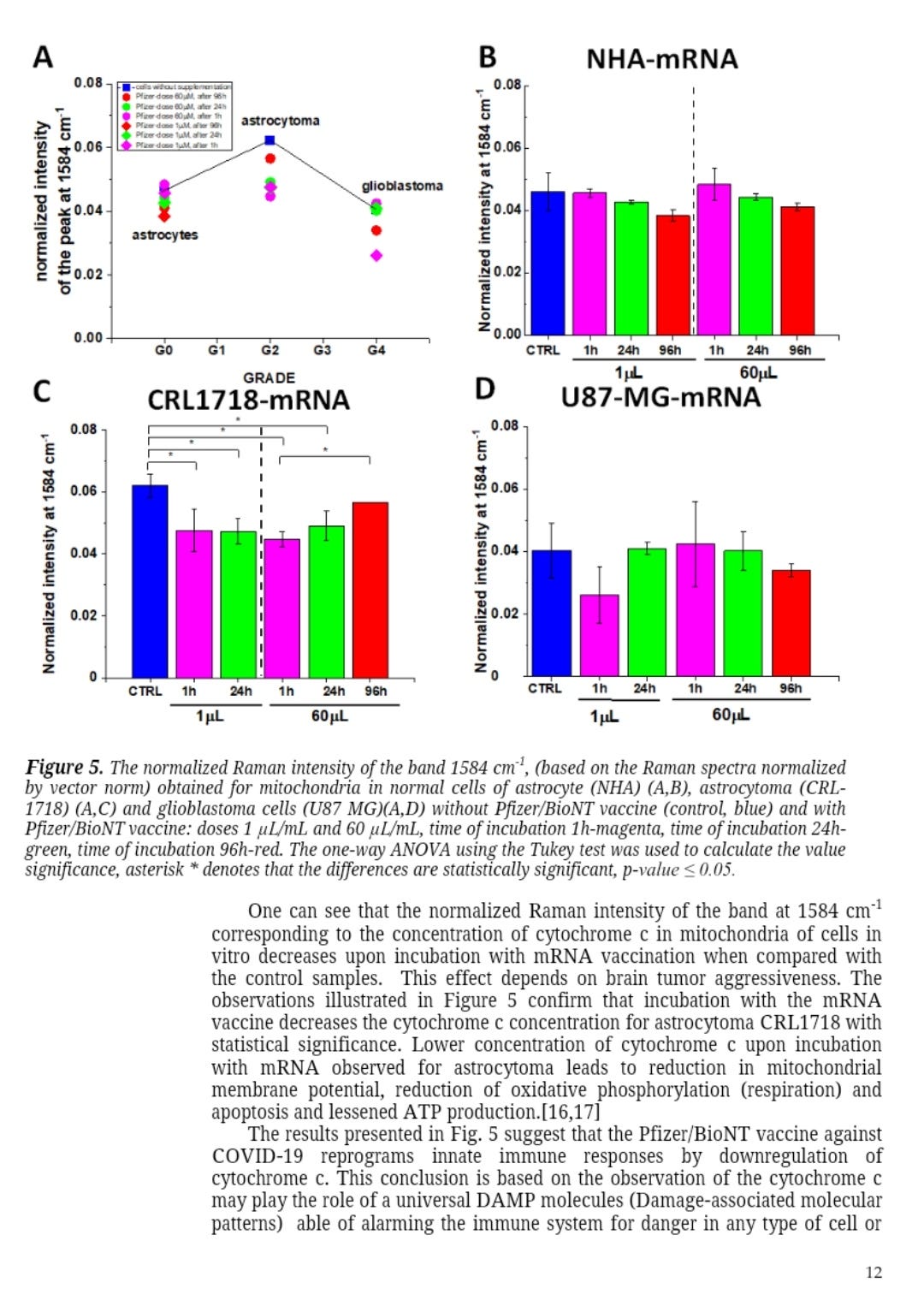
The paper presents the effect of COVID-19 mRNA (Pfizer/BioNT) vaccine on in vitro glial cells of the brain studied by means of Raman spectroscopy and imaging.. The results obtained for human brain normal and tumor glial cells of astrocytes, astrocytoma, glioblastoma incubated with the Covid-19 mRNA vaccine Pfizer/BioNT vaccine show alterations in the reduction-oxidation pathways associated with Cytochrome c. We found that the Pfizer/BioNT vaccine down regulate the concentration of cytochrome c in mitochondria upon incubation with normal and tumorous glial cells. Concentration of oxidized form of cytochrome c in brain cells has been shown to decrease upon incubation the mRNA vaccine. Lower concentration of oxidized cytochrome c results in lower effectiveness of oxidative phosphorylation (respiration), reduced apoptosis and lessened ATP production. Alteration of Amide I concentration, which may reflect the decrease of mRNA adenine nucleotide translocator. Moreover, mRNA vaccine leads to alterations in biochemical composition of lipids that suggest the increasing role of signaling. mRNA vaccine produce statistically significant changes in cell nucleus due to histone alterations. The results obtained for mitochondria, lipid droplets, cytoplasm may suggest that COVID-19 mRNA (Pfizer/BioNT) vaccine reprograms immune responses. The observed alterations in biochemical profiles upon incubation with COVID-19 mRNA in the specific organelles of the glial cells are similar to those we observe for brain cancer vs grade of aggressiveness.
“Recently we showed that the lipid droplets in cancer cells are predominantly filled with TAGs and are involved in energy storage. The lipid droplets in normal cells NHA are filled mainly with retinyl esters /retinol and are involved in signaling, especially JAK2/STAT6 pathway signaling [22]. The results presented in Figure 9 suggest that upon incubation with mRNA increases the role of signaling. Our results support those reported recently that COVID-19 spike protein elicits cell signaling in human host cells, which may have serious implications for Possible Consequences of COVID-19 vaccines.”:
“Our results from Fig. 10 show that apoptosis is reduced upon mRNA vaccine for astrocytoma and glioblastoma which indicate decreased ability to fight against cancer development by programmed cell death.”:
Link to full paper pdf: