The International Criminal Court (ICC)
Democide provides ample cause to invoke the ICC
“Democide is the murder of any person or people by their government, including genocide, politicide, and mass murder. Democide is not necessarily the elimination of entire cultural groups but rather groups within the country that the government feels need to be eradicated for political reasons and due to claimed future threats.[1][2]
According to Rummel, genocide has three different meanings. The ordinary meaning is murder by government of people due to their national, ethnic, racial or religious group membership. The legal meaning of genocide refers to the international treaty on genocide, the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide. This also includes nonlethal acts that in the end eliminate or greatly hinder the group. Looking back on history, one can see the different variations of democides that have occurred, but it still consists of acts of killing or mass murder. The generalized meaning of genocide is similar to the ordinary meaning but also includes government killings of political opponents or otherwise intentional murder. In order to avoid confusion over which meaning is intended, Rummel created democide for this third meaning.”[5]
More:
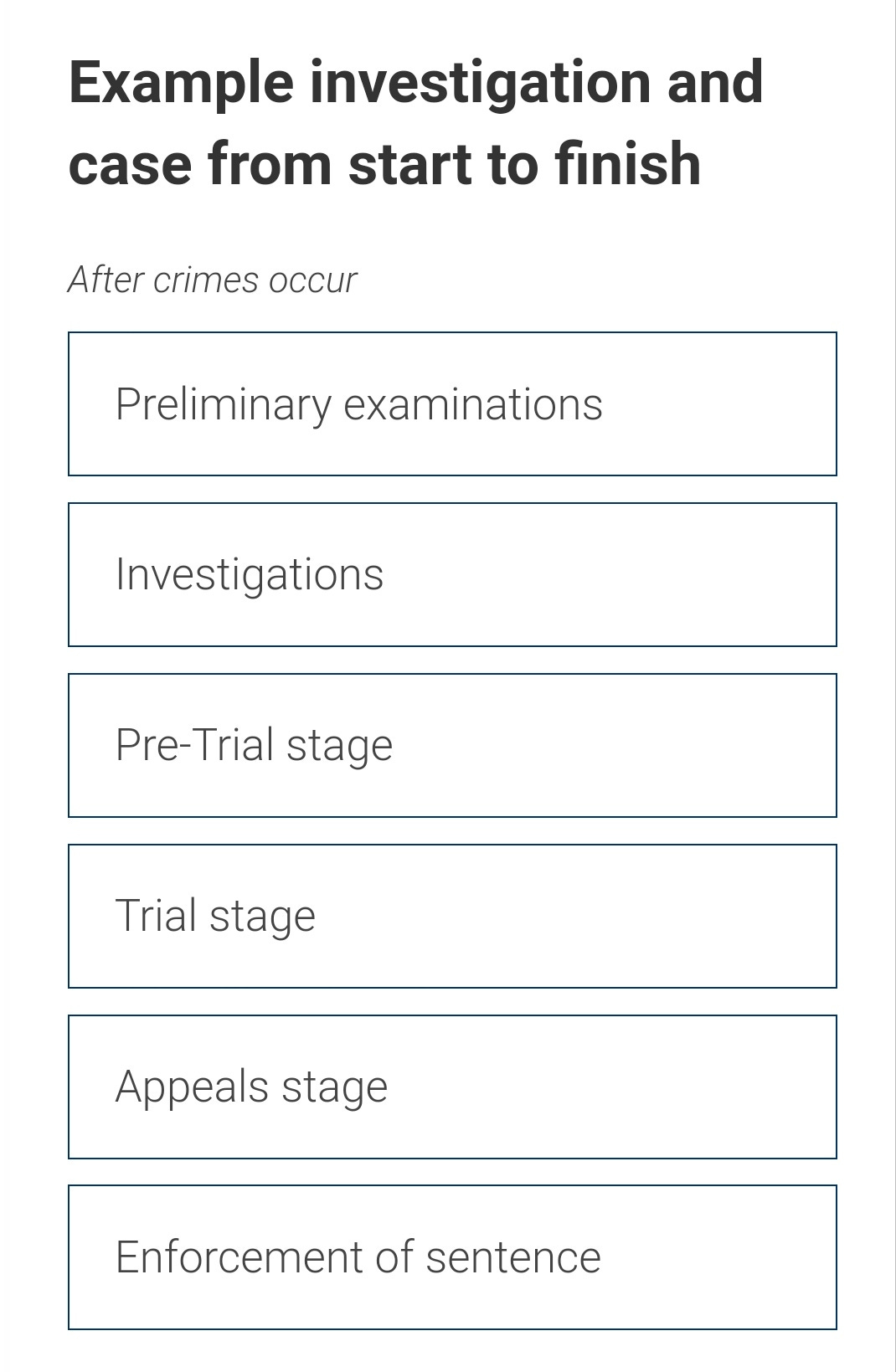
How the Court works
The crimes
The Court's founding treaty, called the Rome Statute, grants the ICC jurisdiction over four main crimes.
First, the crime of genocide is characterised by the specific intent to destroy in whole or in part a national, ethnic, racial or religious group by killing its members or by other means: causing serious bodily or mental harm to members of the group; deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part; imposing measures intended to prevent births within the group; or forcibly transferring children of the group to another group.
Jurisdiction
The Court may exercise jurisdiction in a situation where genocide, crimes against humanity or war crimes were committed on or after 1 July 2002 and:
the crimes were committed by a State Party national, or in the territory of a State Party, or in a State that has accepted the jurisdiction of the Court; or
the crimes were referred to the ICC Prosecutor by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) pursuant to a resolution adopted under chapter VII of the UN charter.
Full article: